For instance, a 10% increase in sales for a company with low DOL might result in a less than 10% increase in EBIT, indicating a more stable, albeit less responsive, profit scenario. As said above, we can verify that a positive operating leverage ratio does not always mean that the company is growing. Actually, it can mean that the business is deteriorating or going through a bad economic cycle like the one from the 2nd quarter of 2020. Investors can come up with a rough estimate of DOL by dividing the change in a company’s operating profit by the change in its sales revenue. In the final section, we’ll go through an example projection of a company with a high fixed cost structure and calculate the DOL using the 1st formula from earlier.
Investors Can Access The Risk
- And the irony of the situation is that there is a tiny margin to adjust yourself by cutting fixed costs in demand fluctuations and economic downturns.
- Now, we are ready to calculate the contribution margin, which is the $250mm in total revenue minus the $25mm in variable costs.
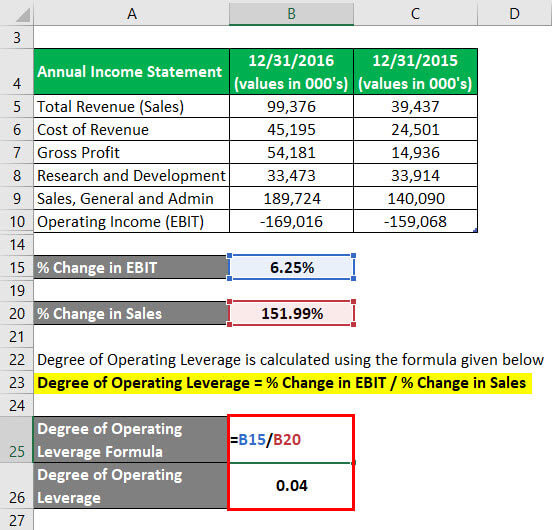
- In other words, operating leverage is the measure of fixed costs and their impact on the EBIT of the firm.
- Learn financial statement modeling, DCF, M&A, LBO, Comps and Excel shortcuts.
Learn financial statement modeling, DCF, M&A, LBO, Comps and Excel shortcuts. For comparability, we’ll now take a look at a consulting firm with a low DOL. An example of a company with a high DOL would be a telecom company that has completed a build-out of its network infrastructure.
How Operating Leverage Can Impact a Business
After the collapse of dotcom technology market demand in 2000, Inktomi suffered the dark side of operating leverage. As sales took a nosedive, profits swung dramatically to a staggering $58 million loss in Q1 of 2001—plunging down from the $1 million profit the company had enjoyed in Q1 of 2000. Operating leverage can tell investors a lot about a company’s risk profile. Although high operating leverage can often benefit companies, companies with high operating leverage are also vulnerable to sharp economic and business cycle swings.
Degree Of Operating Leverage: Explanation, Formula, Example, and More
This happens because firms with high degree of operating leverage (DOL) do not increase costs proportionally to their sales. On the other hand, a high DOL incurs a higher forecasting risk because even a small forecasting error in sales may lead to large miscalculations of the cash flow projections. Therefore, poor managerial decisions can affect a firm’s operating level by leading to lower sales revenues. Operating leverage is a financial efficiency ratio used to measure what percentage of total costs are made up of fixed costs and variable costs in an effort to calculate how well a company uses its fixed costs to generate profits. Conversely, Walmart retail stores have low fixed costs and large variable costs, especially for merchandise. Because Walmart sells a huge volume of items and pays upfront for each unit it sells, its cost of goods sold increases as sales increase.

What does a high DOL indicate?
Higher financial leverage represents the high volatility of a company’s earnings per share by a change in EBIT. The degree of operating leverage (DOL) measures how much change in income we can expect as a response to a change in sales. In other words, the numerical value of this ratio shows how susceptible the company’s earnings before interest and taxes are to its sales. The DOL is calculated by dividing the contribution margin by the operating margin.
Since 10mm units of the product were sold at a $25.00 per unit price, revenue comes out to $250mm. Later on, the vast majority of expenses are going to be maintenance-related (i.e., replacements and minor updates) because the core infrastructure has already been set up. A company with a high DOL coupled with a large amount of debt in its capital structure and cyclical sales could result in a disastrous outcome if the economy were to enter a recessionary environment. Or, if revenue fell by 10%, then that would result in a 20.0% decrease in operating income. Let us take the example of Company A, which has clocked sales of $800,000 in year one, which further increased to $1,000,000 in year two.
We may earn a commission when you click on a link or make a purchase through the links on our site. All of our content is based on objective analysis, and the opinions are our own.
Another way to control this operational expense line item is to reduce unnecessary expenses, especially during slow seasons when sales are low. As a hypothetical example, say Company X has $500,000 in sales in year one and $600,000 in sales in year two. In year one, the company’s operating expenses were $150,000, while in year two, the operating expenses were $175,000. The most authentic calculation method after the percentage change method is the ‘Sales minus Variable costs’ method.
In this case, it will be the 1st quarter, 2020 and the2nd quarter, 2020. For the particular case of the financial one, our handy return of invested capital calculator can measure its influence on the business returns. Furthermore, another important distinction lies in how the vast majority of a clothing retailer’s future costs are unrelated to the foundational expenditures the business was founded upon.
With positive (i.e. greater than zero) fixed operating costs, a change of 1% in sales produces a change of greater than 1% in operating profit. If the composition of a company’s cost structure is mostly fixed costs (FC) relative to variable costs (VC), the business model of the company is implied to possess a higher degree of operating leverage (DOL). For example, a software business has greater fixed costs in developers’ salaries and lower variable costs in software sales. In contrast, a computer consulting firm charges its clients hourly and doesn’t need expensive office space because its consultants work in clients’ offices. This results in variable consultant wages and low fixed operating costs.
With each dollar in sales earned beyond the break-even point, the company makes a profit, but Microsoft has high operating leverage. For example, Company A sells 500,000 products for a unit price of $6 each. Operating leverage can also be measured in terms single vs double taxation of change in operating income for a given change in sales (revenue). A financial ratio measures the sensitivity of a firm’s EBIT or operating income to its revenues. Operating leverage and financial leverage are two very critical terms in accounting.
